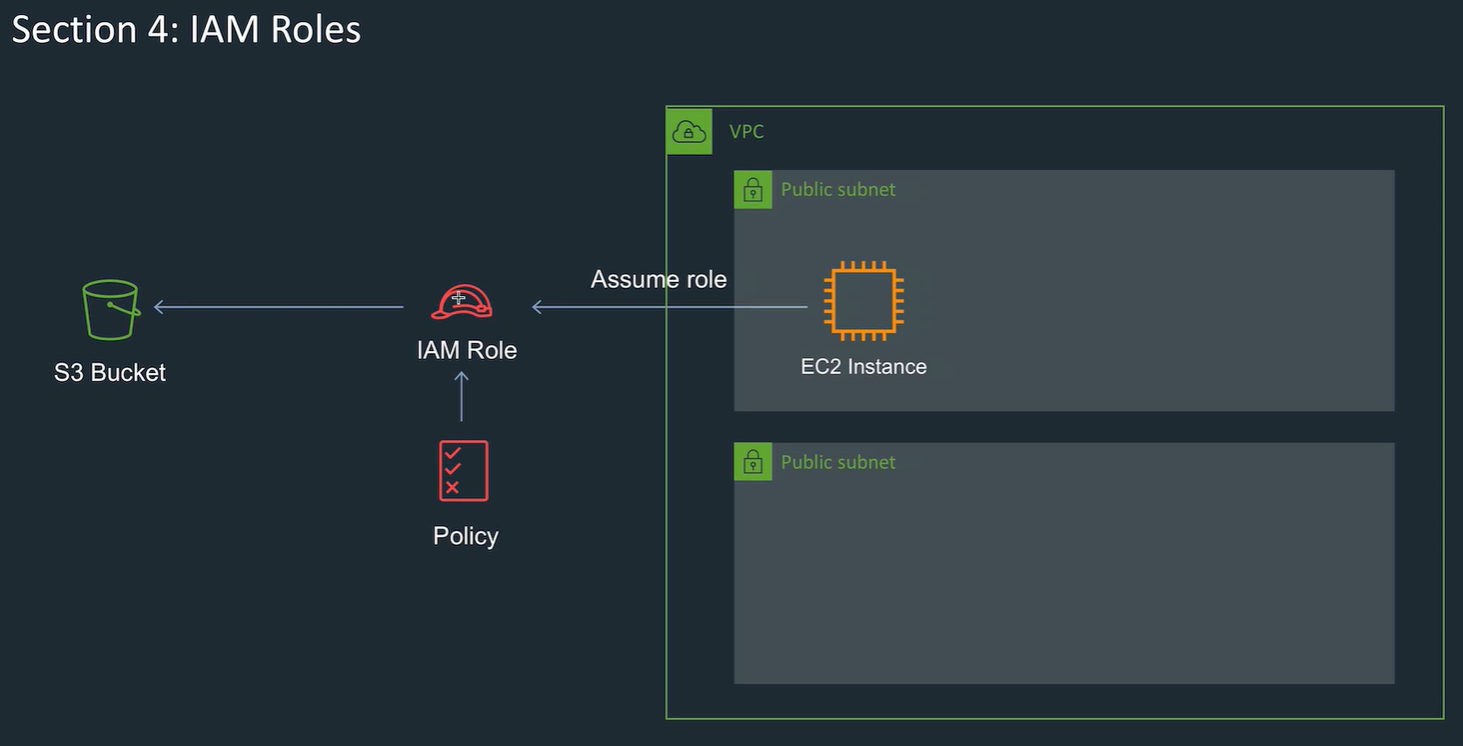

Create a role, give it a policy. EC2 instance can assume a role. Gives short term permissions.
Single end point, lots of targets.
High availability and fault tolerance.
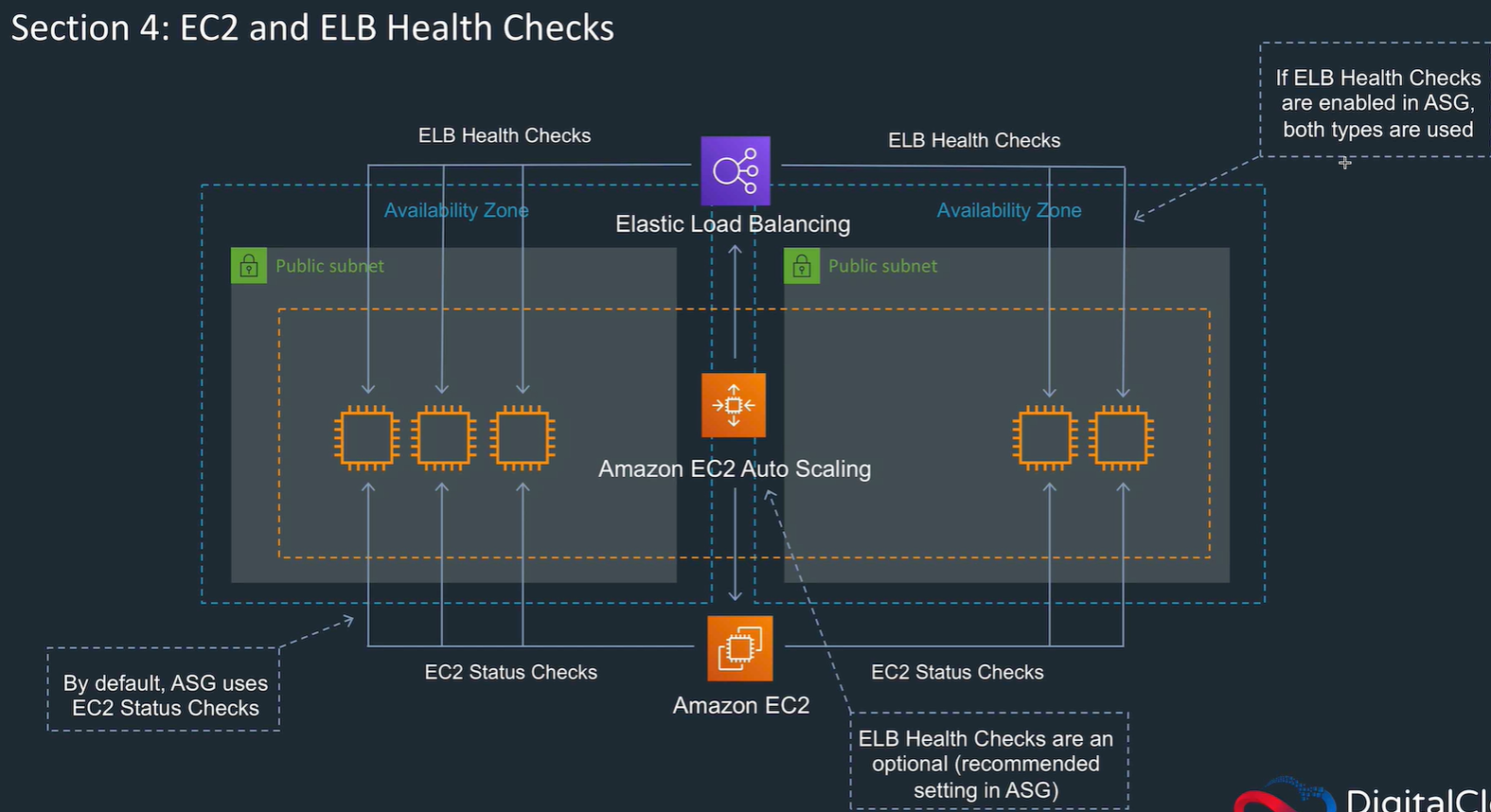
Health checks to see if instances available.
Set up DNS record in Route 53 to send traffic on a DNS name to the ALB
ELB scales by adding ELB nodes in your subnets
ELB security groups need to be reachable, and need to be able to run health checks on targets.

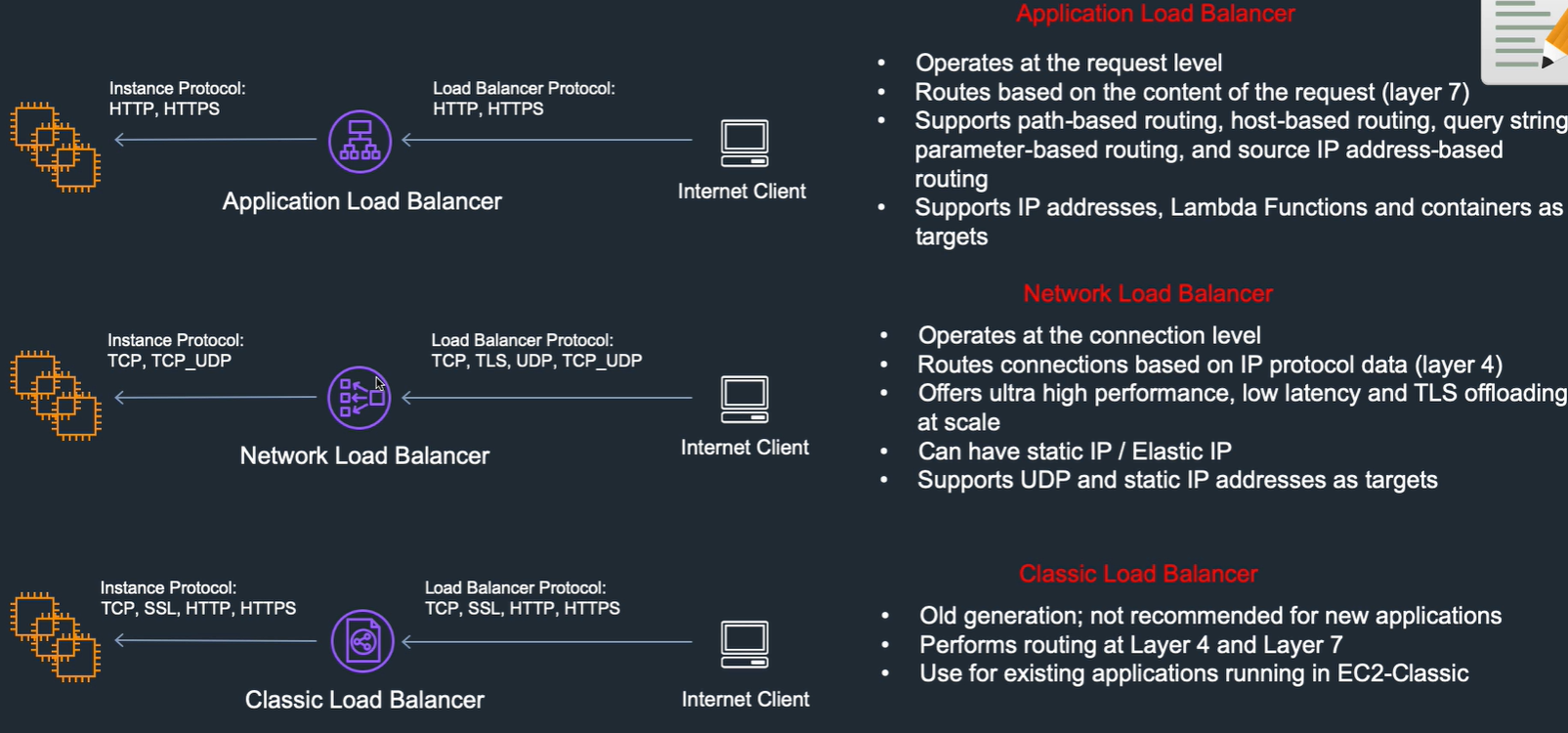
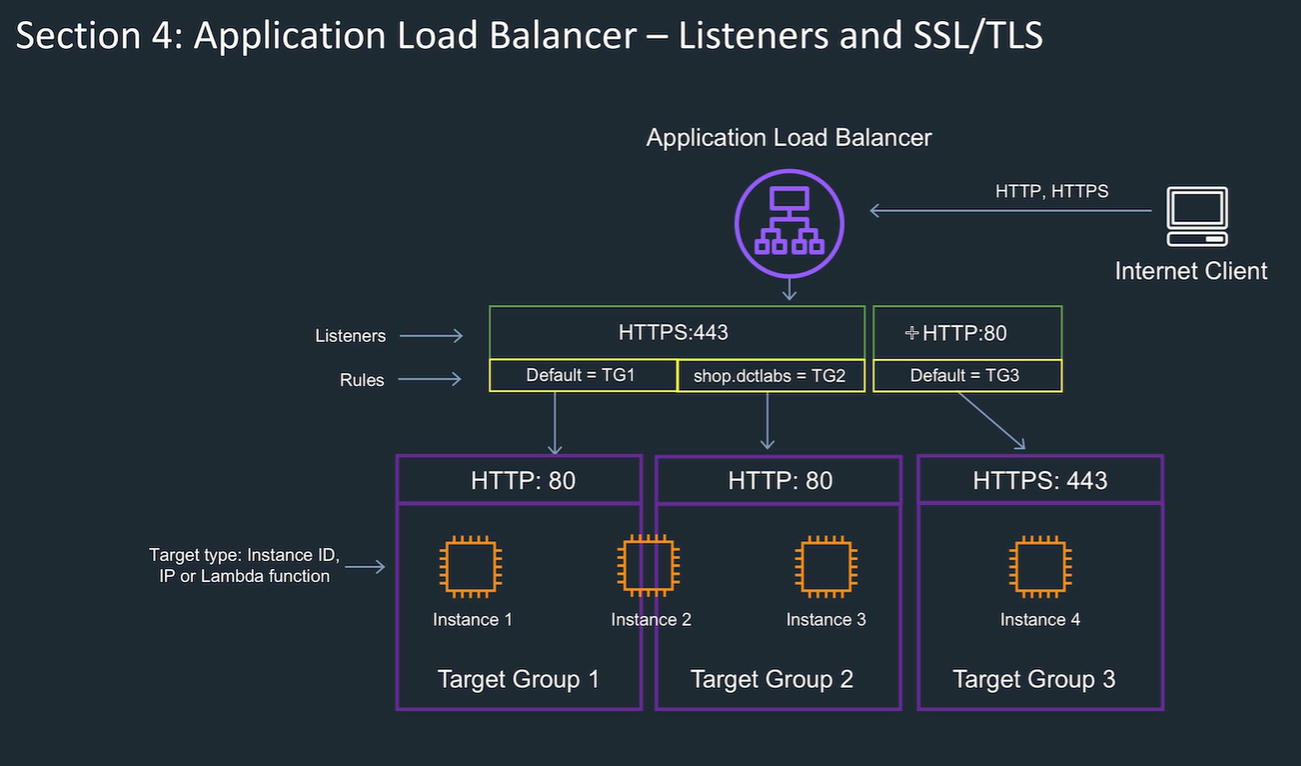
Level 7, HTTP listeners, request level
Query string
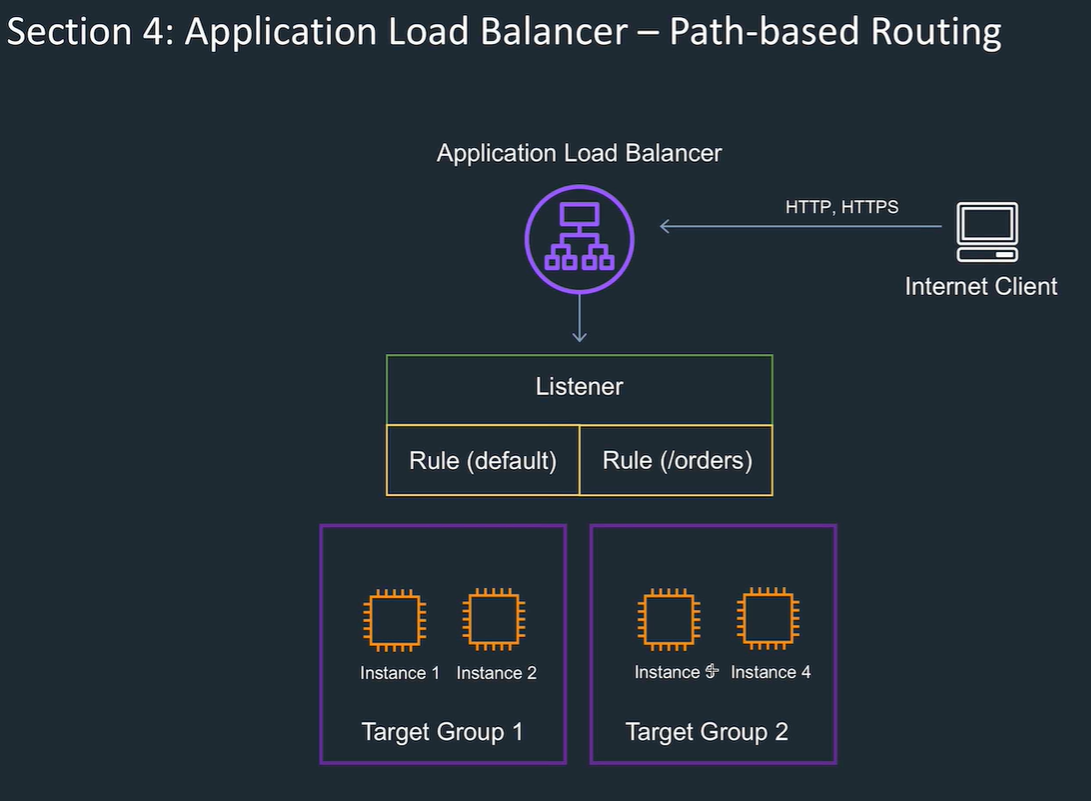
Supports path and host based routing.
IP addresses, Lambda functions, etc
Level 4. TCP listeners, connection level Ultra high performance, very low latency, high number of connections. Can have static ip address or ELP
Old generation
Register instances in target groups Say how many need to be awake Target group is the group of instances that the traffic is distributed to. (this can be an auto scaling set) Can send traffic to different target groups depending on the path or host in the HTTP headers. Can choose to make client sessions round robin / least queue or sticky to a EC2 instance.
Cloudwatch every 1 minute by default
Set options in load balancer to store logs to S3.
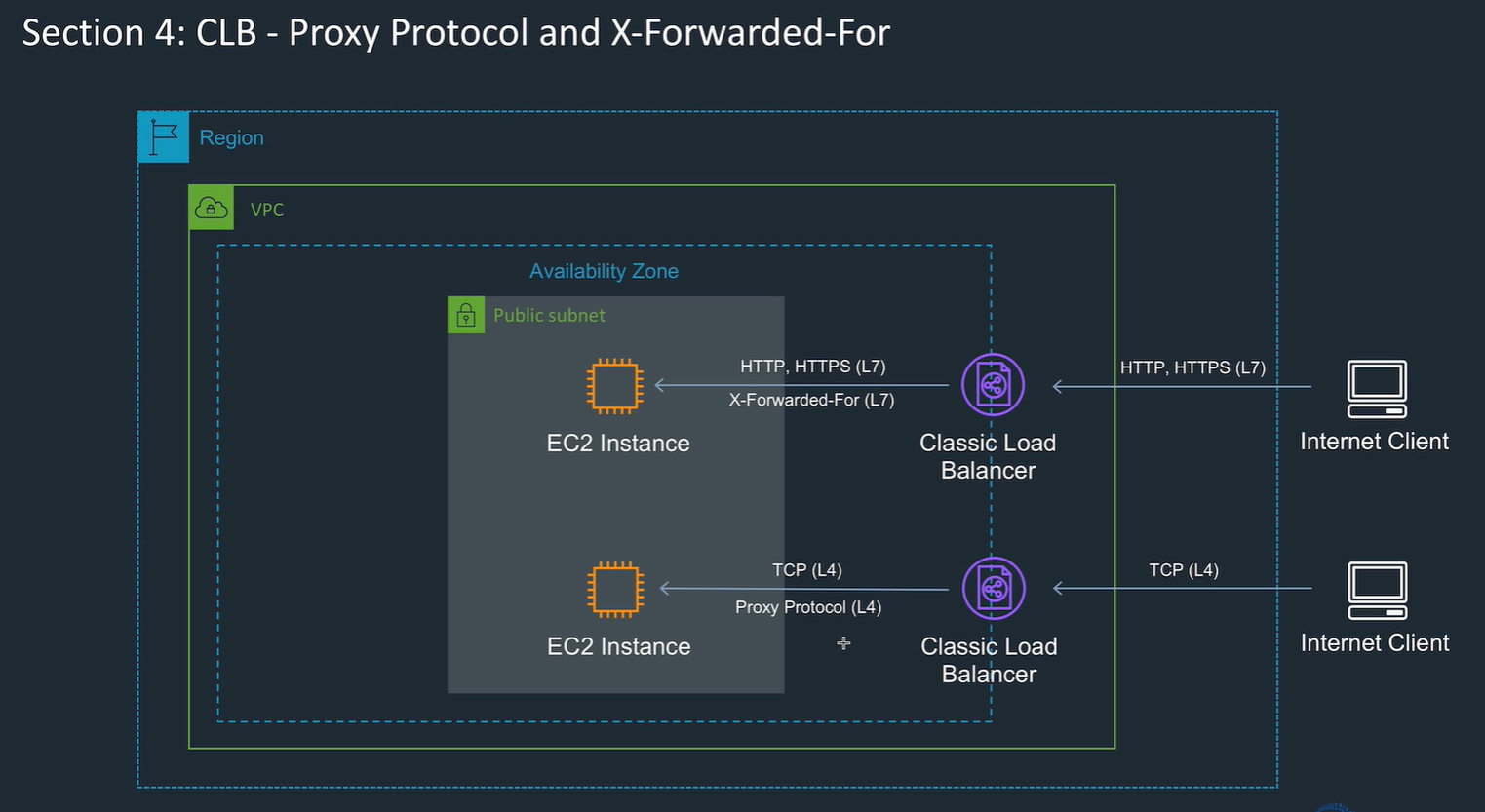
The logs can record the source IP address of the client through the stack, not just e.g. the last layer originating the request.
Both of these pass on the source IP address so it's in logs.
Need to use Proxy protocol (layer 4 in NLB) or X-forwarded-For (Layer 7 in ALB) to do this.
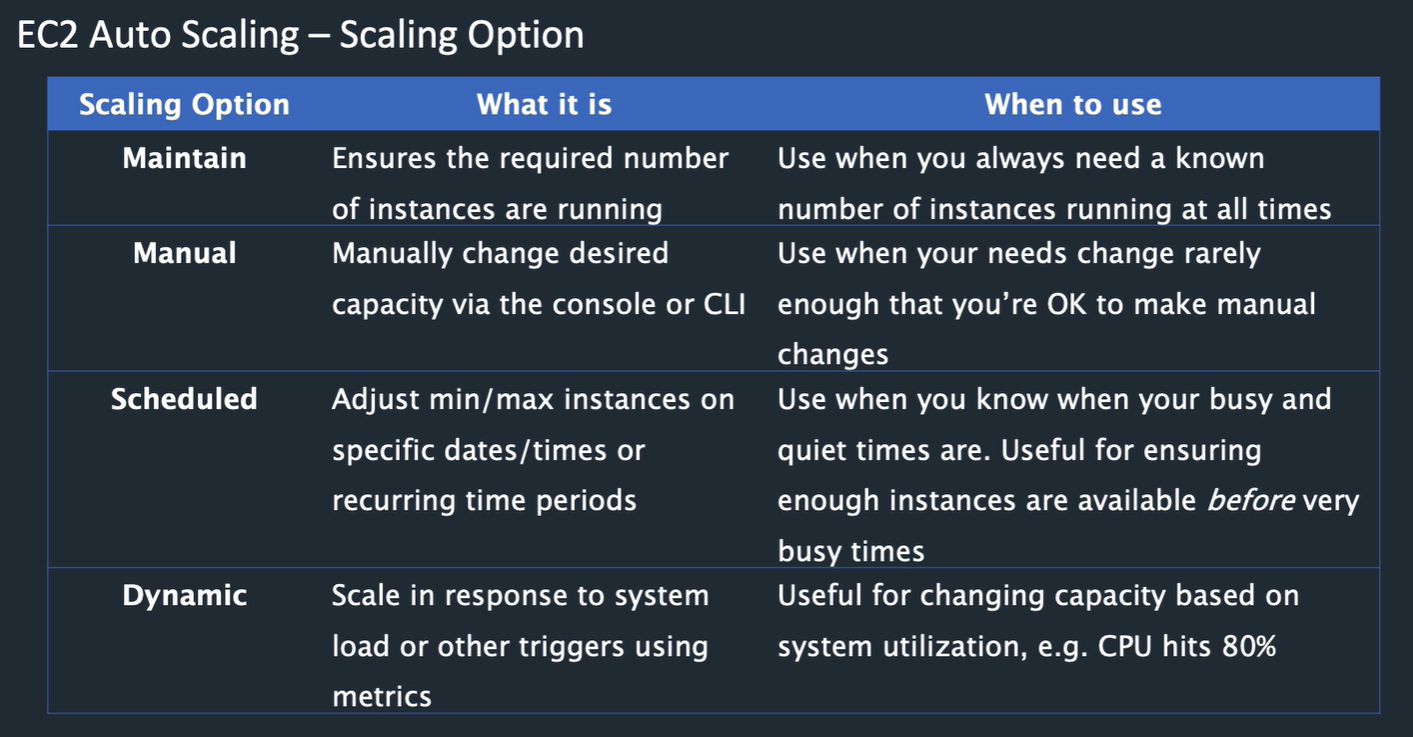
Scaling options:
Scaling policies:
Termination policies:

Features:
Install epel from amazon-linux-extras to get stress environment
sudo amazon-linux-extras install epel -y
sudo yum install stress -y
stress -c 8
Set AMI, instance type, key pair, network interfaces.
Can create from an existing instance.
Has versions.
Can combine purchase options: e.g. spot and on demand
Default policy chooses which instance to terminate (can choose a different policy)
Can suspend certain behaviors e.g. termination, replace unhealthy Cooldown period: Warmup period:
ELB distributes traffic between zones, using ELB Nodes (you don't see these). With cross zone off, each zone gets e.g. 50% of traffic With cross zone on, each zone gets traffic relating to the numbers of instances.
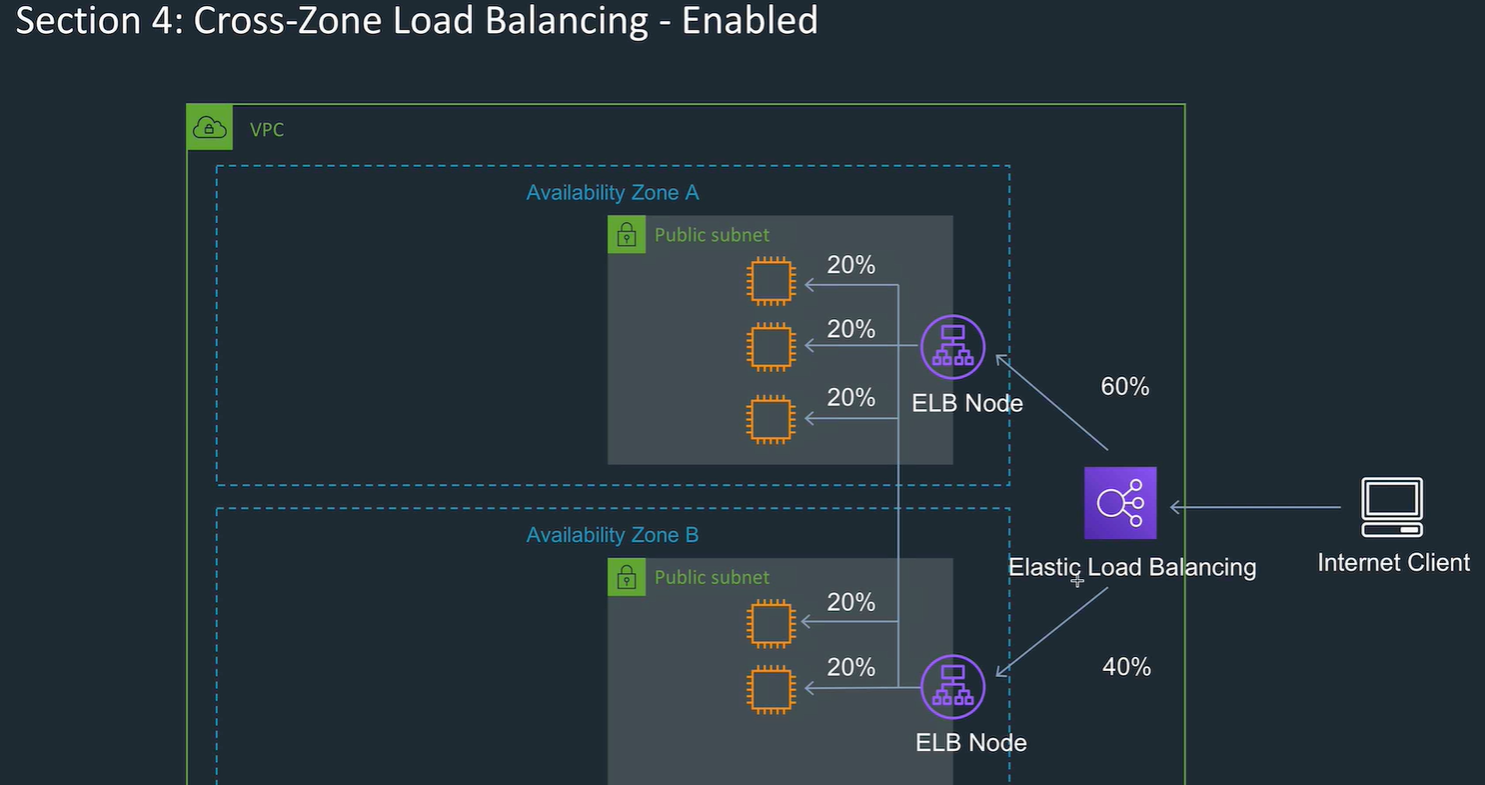
Cross zone load balancing is always enabled for ALB. Cross zone load balancing is optional enabled for NLB.
Sticky sessions: ALB only. uses cookie on client side.
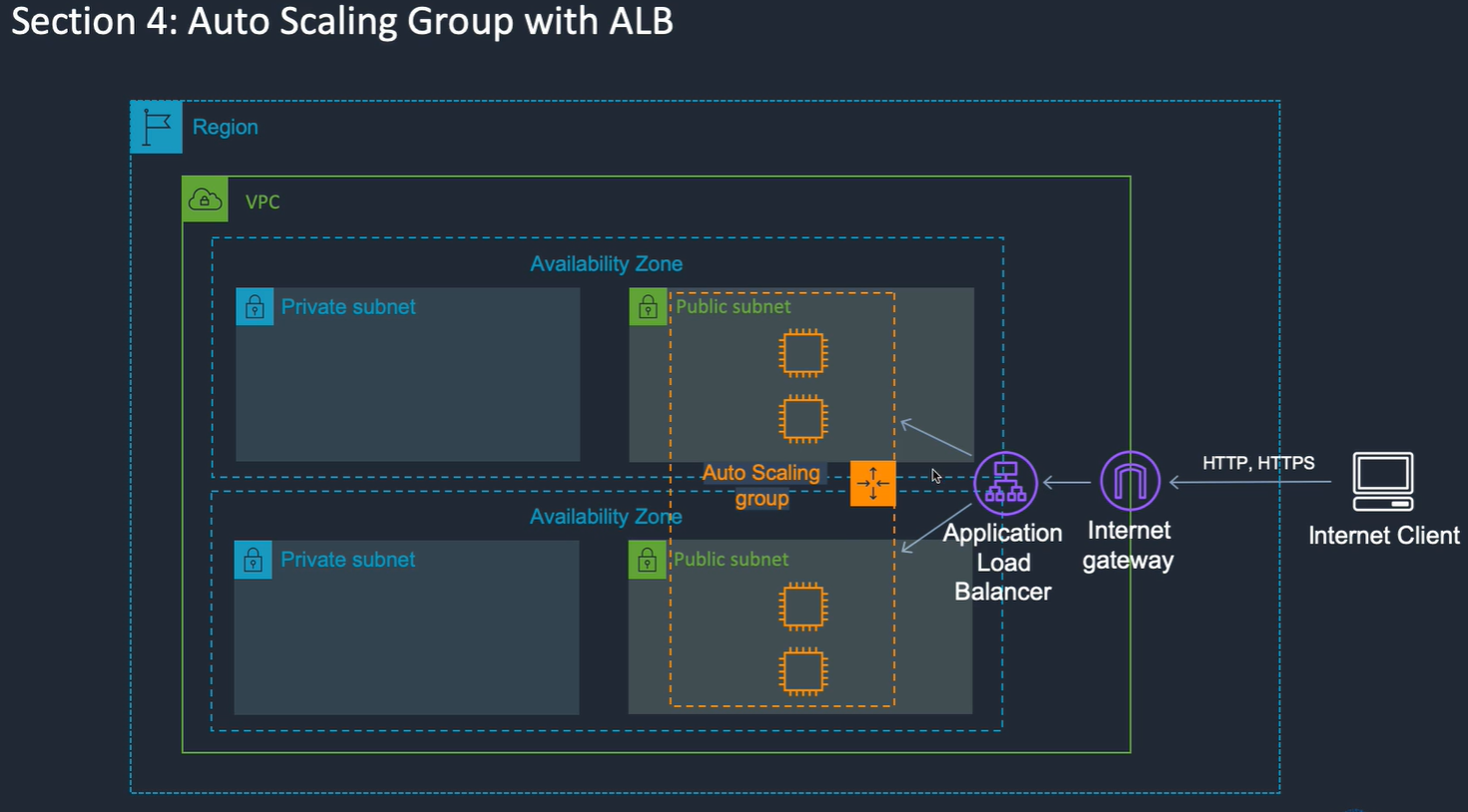
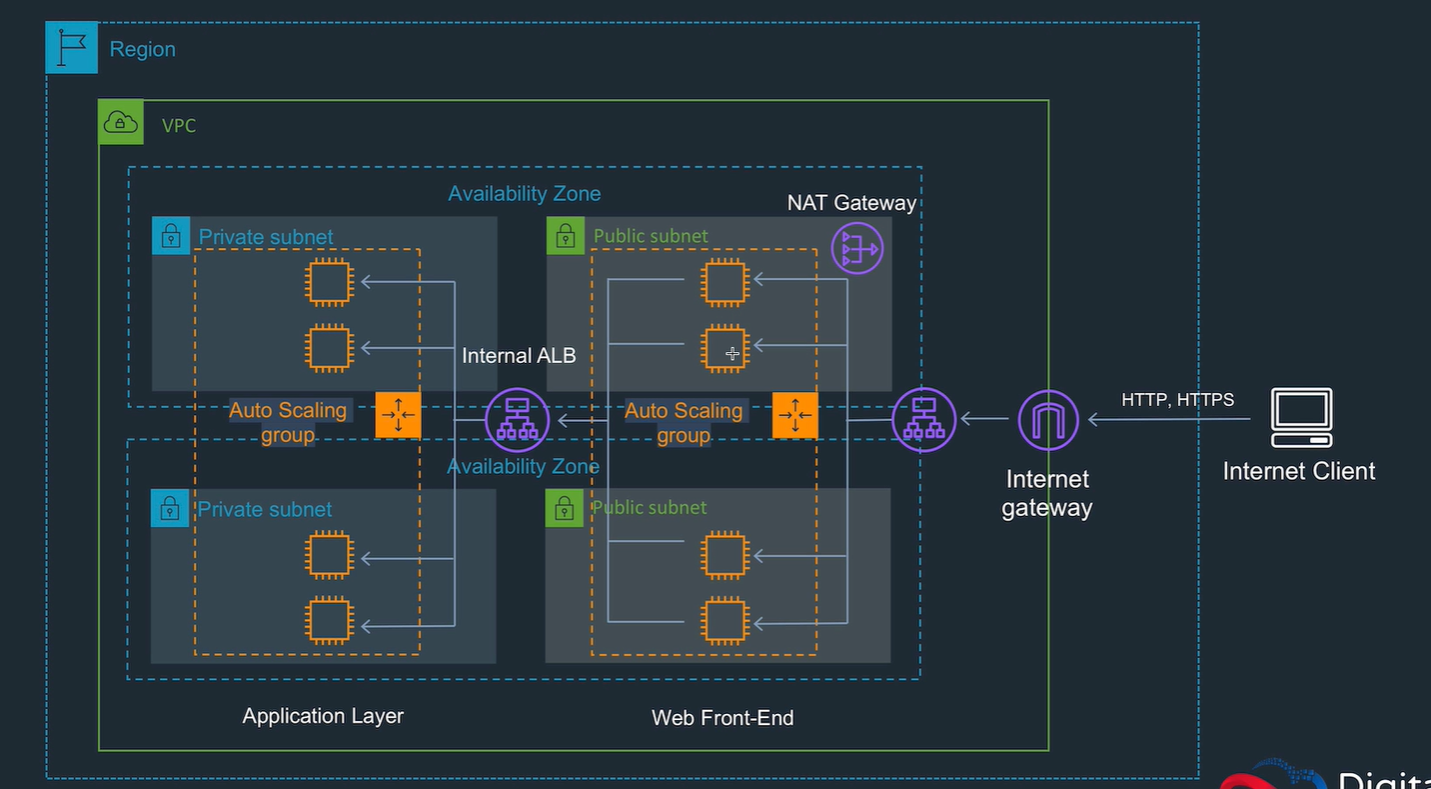
Want ALB to listen on 80 to anything Want EC2 instances in private subnet Best to set up SGs so ALB accepts any traffic on port 80, but only sends to private SG. Instances in private subnet in an SG to only accept traffic from the public SG.
Create a couple of private subnets in different AZs.
Add nat gateway with elastic IP address.
Create route table to allow traffic between subnets, and also outbound traffic to go to net gateway.
Create ASG with instances in private subnets.
simple secure SG setup:
Full solution:
better Security group configuration for this:
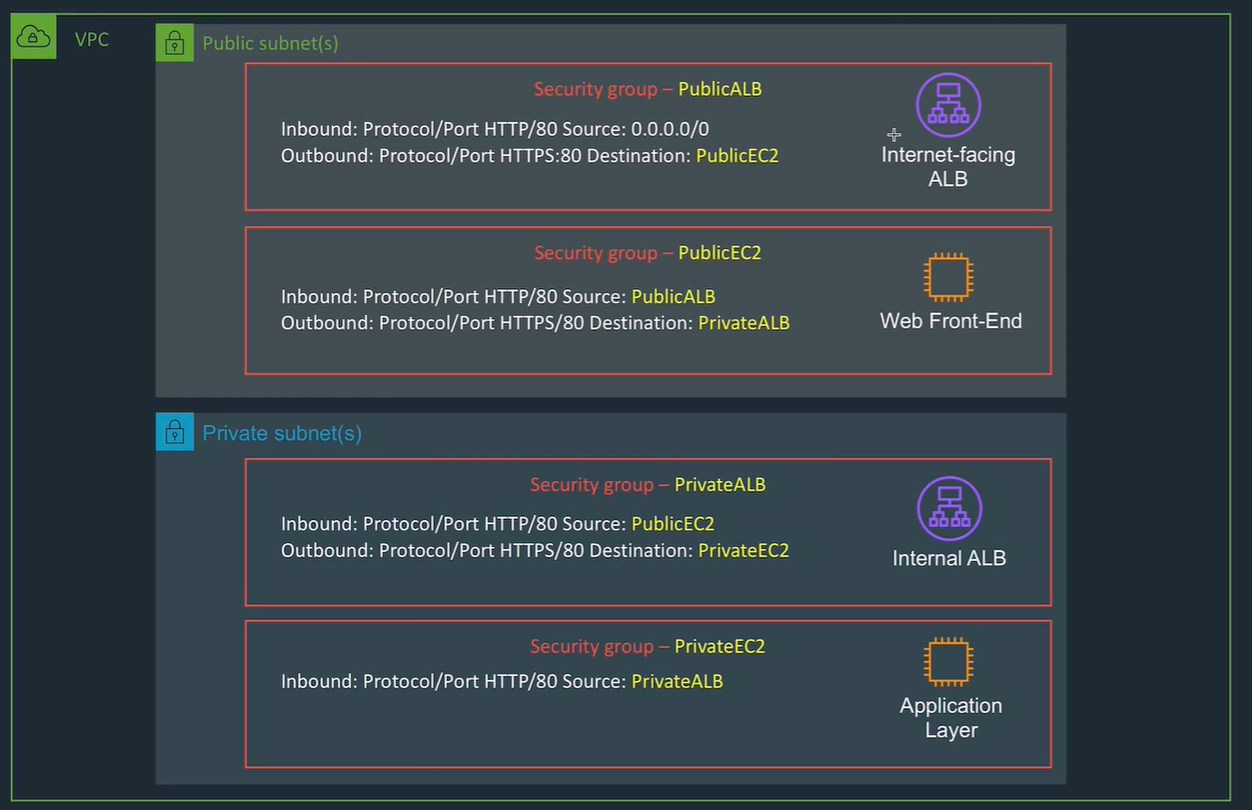
And so on for e.g. database layer.