AWS logging and Monitoring
Overview
Cloudtrail: auditing and API activity
- Every interaction over API, console etc is an api call
- More about auditing and security
- More low level
- Log from multiple accounts
- Logs stored to S3 or cloudwatch indefinitely
- No alarms: use cloudwatch
Cloudwatch: Monitoring
- Performance monitoring
- Operational health
- Alarms
- Metrics
- Log from multiple accounts
- Logs stored indefinitely
- Alarm history for 14 days
Cloudwatch detail
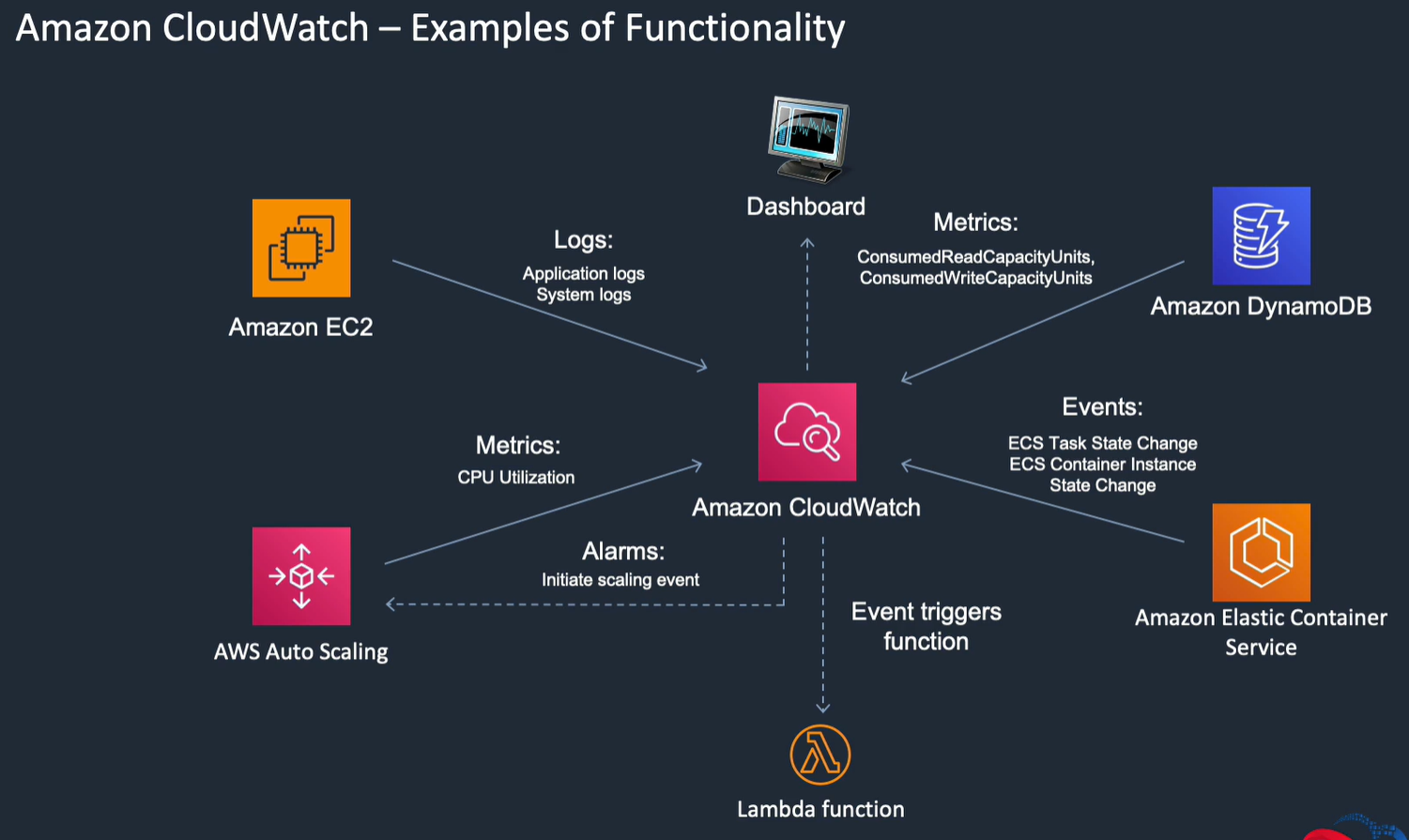
- Namespace: container for cloudwatch metrics, so different resource groups get separate metrics
- Metrics: time ordered. Can't be deleted but expire after 15 months, can create custom metrics
- Different metrics for each service
- Dimensions: subdivision below namespace. E.g. EC2 has various dimensions, autoscaling is one.
- Statistics: metrics aggregated over time, e.g. average
- Alarms: watch a metric and automatically trigger actions. Alarms need a state change and maintained for an amount of time, e.g. CPU > 80% for 3 mins
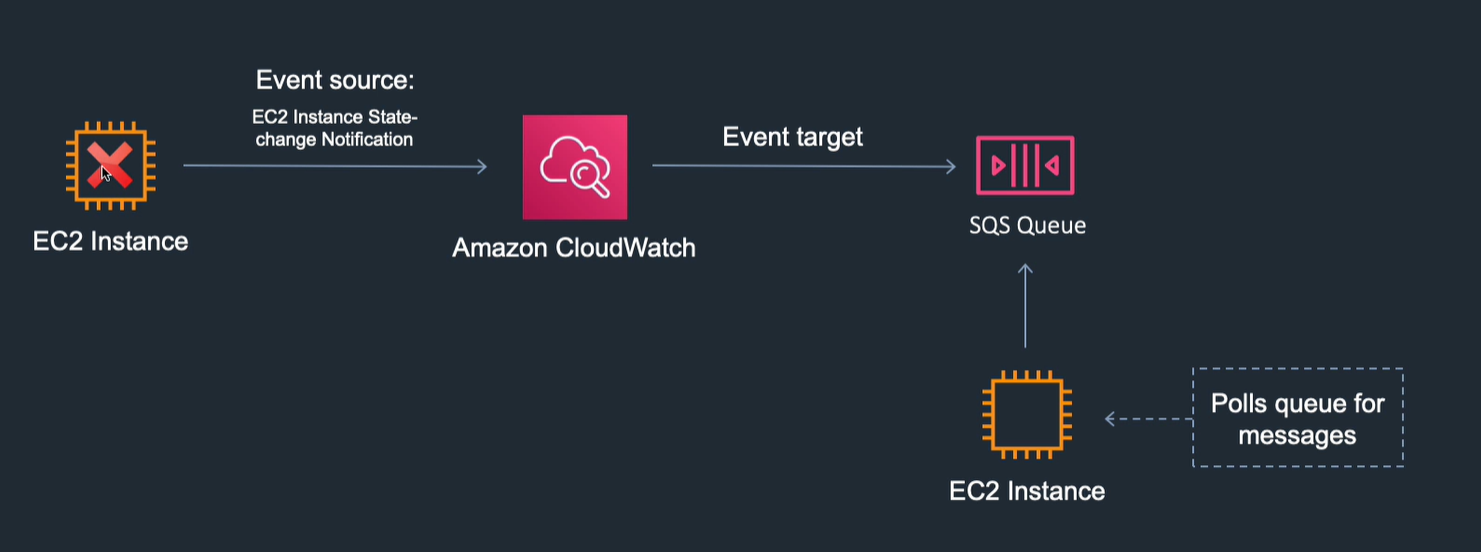
- Events: delivers near real time stream of system events. Can use to schedule from e.g. cron. Can route them to a target, e.g. Lambda. Specify event source, state change, and set target.
Creating a custom metric in EC2
- e.g. Memory is not a standard metric for EC2.
- Set up custom metric with crontab calling shell script to get the memory and do an AwS cli call.
- EC2 doesn't send logs by default. If you want to get application logs to cloudwatch need to install Cloudwatch application agent. Lambda has logs enabled.
Event example
Cloudtrail Detail
Audit log for resource changes.
Create a trail, that delivers log files to S3 bucket.
Enables governance, compliance, operational risk auditing
- trail types: all regions, or single region.
- Management events: (also known as control plane events) include security changes, registering devices, logging changes.
- Data events: (data plane operations) higher volume.
AWS Config
- Gives you a resource inventory.
- Configuration history for each resource.
- Alerts you if resources change from that state.
- Enables security and governance
- Config is about point in time changes.
- Cloudtrail tells you who changed it, config tells you what the config was.
Rules examples:
- check all EC2 have detailed monitoring enabled
- check all security groups are used, check all network interfaces are attached to a security group
Remediation actions:
There are lots, including e.g.
- run lambda
- stop EC2
- delete security group
Gives you a file per resource in S3


